Push notifications
User permission flow for web push Ensure your Service Worker path and scope are correct
Requirements
- HTTPS
- Valid VAPID public key in
push_config.key - Service Worker path (
push_serviceworkerorservice_worker_path) and scope
Register via config
Hood('init', 'TAG', {
push_config: {
key: 'BExxx...VAPID...',
push_serviceworker: '/sw.js',
serviceWorkerScope: '/'
}
})
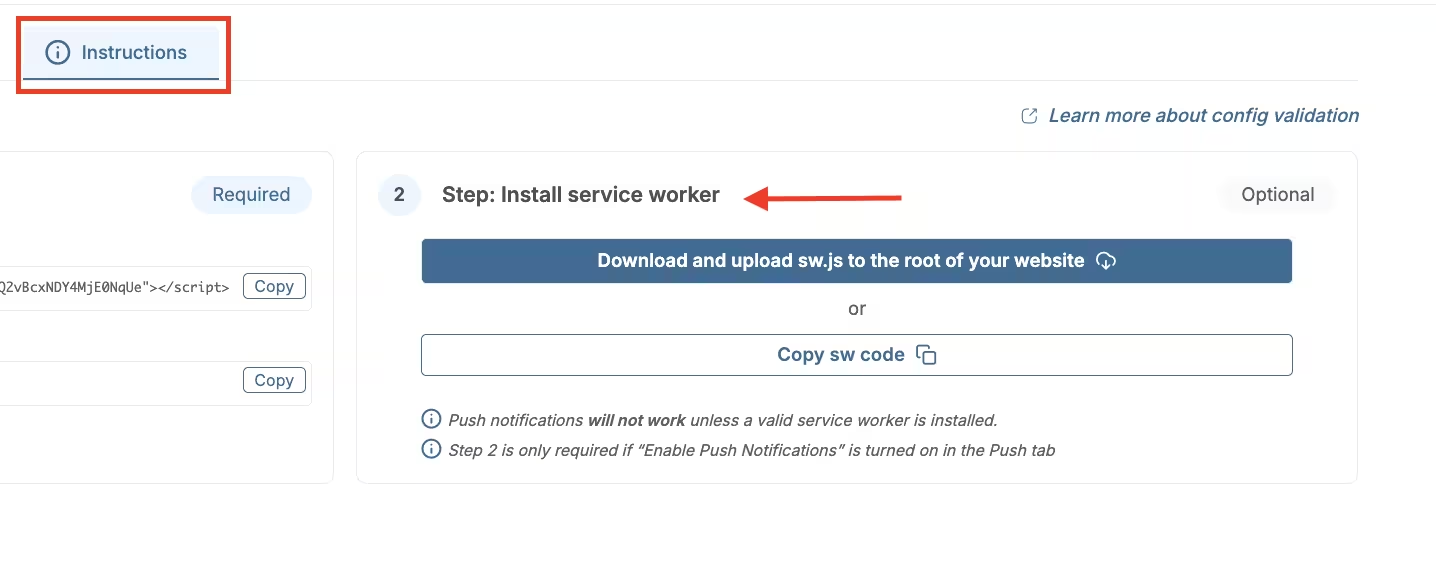
The SDK registers the SW, checks existing subscription, and repairs it if VAPID key changed.
Permission states
Internal states map to browser values: granted, denied, closed/prompt, plus auto‑block heuristics (auto-block, close-block). Subscribe to updates:
Hood('pushstatus', state => { console.log('push state', state) })
Requesting permission
Hood('pushrequestpermission', () => {
console.log('native prompt shown')
})
The SDK tracks prompt outcomes and subscribes the user via PushManager when granted.
Showing a notification
Hood('pushmessage', { title: 'Welcome', options: { body: 'Thanks!' } })
AMP support
When loaded with data-amp="1", the SDK uses an AMP bridge to communicate with SW and proxy subscribe calls.
Prompts as modals
You can define push_config.prompts as modal configs and use triggers/filters to decide when to show soft prompts before native prompt.
Storage keys
- Local:
webpush_dismissals, push‑enabled flags per site (pushorpsh<hash>when subdomain subscription is enabled) - Session: used for temporary analytics/session data
